The Impact of Processed Foods on Health
In today’s fast-paced world, processed foods have become a staple in many diets. They offer tempting convenience but often sacrifice nutrition.
What exactly are processed foods, and why do they dominate your meals? This exploration delves into their definition, the various types available, and the potential health risks that come with their consumption. You ll uncover why they are so popular and receive practical tips to help you limit their intake.
Discover the numerous benefits of adopting a whole foods diet, which can significantly enhance your health and well-being. Join us to understand the impact processed foods have on your life!
Contents
- Key Takeaways:
- What are Processed Foods?
- The Negative Effects of Processed Foods
- Health Risks and Concerns
- Why are Processed Foods Popular?
- Factors Contributing to Consumption
- How to Limit Processed Foods in Your Diet
- Tips for Reducing Intake
- The Benefits of a Whole Foods Diet
- Frequently Asked Questions
- What are processed foods and how do they differ from unprocessed foods?
- How do processed foods impact our health?
- Can processed foods be part of a healthy diet?
- How do processed foods affect weight and weight loss?
- Are there any benefits to consuming processed foods?
- How can I reduce my consumption of processed foods?
Key Takeaways:

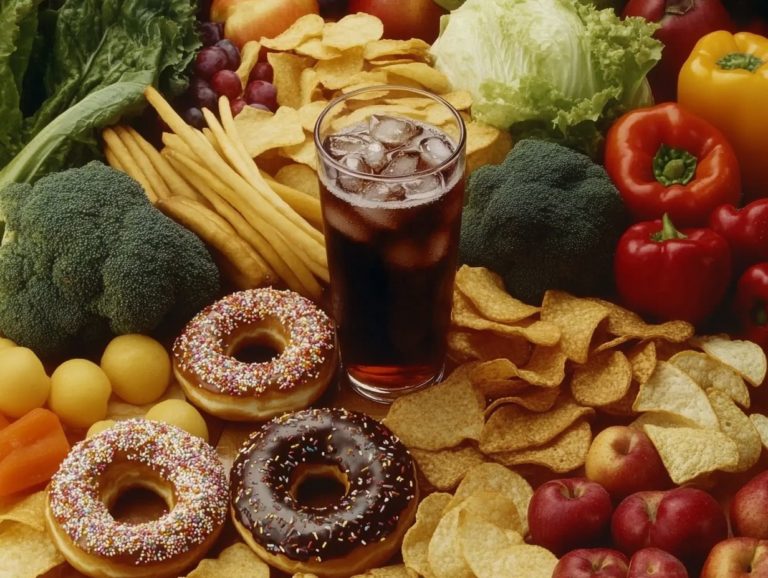
Processed foods are defined as food products that have undergone significant changes from their original form. They include types such as canned, frozen, or packaged options. These foods are often high in calories, unhealthy fats, and added sugars, leading to negative effects on health.
The consumption of processed foods is linked to an increased risk of obesity, heart disease, and other chronic conditions. They are also low in nutrients, contributing to poor overall health.
Processed foods are popular due to convenience, affordability, and taste. However, consumers should be aware of the potential health risks and make an effort to limit their consumption.
What are Processed Foods?
Processed foods refer to items that have been altered from their natural state through various methods, such as canning, freezing, or adding preservatives. While these changes can improve shelf life, convenience, and flavor, they may also reduce the nutritional value of the original food.
The World Health Organization classifies processed foods into several categories: minimally processed, processed culinary ingredients, and ultra-processed foods. Understanding these distinctions is essential for making informed dietary choices that align with your health goals.
Definition and Types
The categorization of processed foods follows the NOVA classification, which distinguishes between minimally processed foods, processed culinary ingredients, and ultra-processed foods. Understanding these categories offers valuable insights into your dietary choices and their potential health impacts.
Minimally processed foods, like fresh fruits and vegetables, retain most of their nutritional value. In contrast, processed culinary ingredients such as oils and sugars are often added to enhance flavor but can lead to increased calorie consumption.
Ultra-processed foods, characterized by artificial additives, preservatives, and multiple processing steps, pose significant health risks. They are linked to chronic diseases such as obesity, diabetes, and heart disease. This classification helps you make more informed choices, ultimately steering you toward better health outcomes.
The Negative Effects of Processed Foods
The consumption of processed foods is closely linked to a range of health risks, including a higher likelihood of chronic diseases like obesity, diabetes, and heart disease.
These concerns increase due to the presence of added sugars, unhealthy fats, and various food additives found in ultra-processed options. Research reveals that the obesity epidemic closely correlates with dietary patterns favoring processed ingredients over whole foods, leading to a considerable loss of essential nutrients.
Summary: Processed foods can harm your health by increasing the risk of chronic diseases while offering little nutritional value. Being aware of these risks can help you make better dietary choices.
Start making informed choices today for a healthier tomorrow!
Health Risks and Concerns

The health risks associated with processed foods are concerning. They are particularly linked to obesity, diabetes, and heart disease.
These foods often contain high levels of added sugars, unhealthy fats, and sodium. This significantly contributes to the alarming rise in obesity rates. Over 650 million adults worldwide are currently affected, as reported by the World Health Organization.
Processing methods can strip essential nutrients, leading to deficiencies of vitamins and minerals that are crucial for maintaining overall health.
Studies show that diets rich in processed foods can raise the risk of developing type 2 diabetes by as much as 30%.
The lack of strict food safety rules in some areas allows harmful additives into our food supply, intensifying these health concerns.
Why are Processed Foods Popular?
Processed foods have become incredibly popular due to their convenience, affordability, and the fast-paced lives many of us lead today.
These ready-made meals offer quick solutions that fit perfectly into our busy schedules and food budgets, accommodating various dietary preferences.
The World Health Organization highlights that these foods are often heavily marketed, making them attractive for those seeking effortless meal options.
Factors Contributing to Consumption
Several factors contribute to the increased consumption of processed foods. These include convenience, affordability, and aggressive marketing tactics used by food manufacturers.
It’s easy to choose quick meals when you’re busy, but your health deserves better! Many of us prioritize quick meal solutions over fresh alternatives, making processed options particularly appealing.
Innovative advertising techniques target various demographics, leading us to associate convenience with modern living.
For communities facing food security challenges, processed foods often emerge as the most available options. They may offer a semblance of nutrition, even if this comes at the expense of dietary quality.
These intertwined elements show how changing marketing practices and lifestyle habits shape our eating patterns today.
How to Limit Processed Foods in Your Diet
Limiting processed foods in your diet can greatly improve your overall health and well-being. By focusing on unprocessed foods, you fuel your body with essential nutrients and vitamins.
To start, read food labels carefully. This will help you identify processed ingredients and make mindful choices that highlight whole, nutrient-dense options.
Tips for Reducing Intake

To effectively reduce your intake of processed foods, try these practical strategies:
- Plan your meals and cook at home using unprocessed ingredients.
- Spend a few hours each week cooking at home to save time during busy weekdays.
- Experiment with cooking techniques like steaming, roasting, or grilling to retain more nutrients and enhance flavors.
- Read food labels critically to avoid hidden sugars, preservatives, and unhealthy fats.
- Emphasize whole, unprocessed ingredients to foster healthier eating habits.
These steps can lead to sustained energy levels, an improved mood, and a lower risk of chronic diseases.
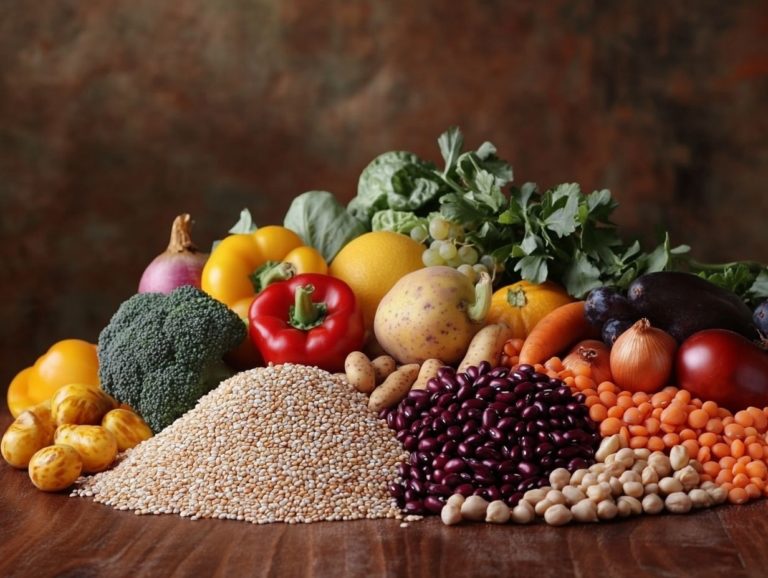
The Benefits of a Whole Foods Diet
Embracing a whole foods diet, centered on unprocessed foods, offers numerous health benefits. This includes a significant reduction in the risks linked to processed foods.
By prioritizing whole foods in your meals, you can enhance your dietary habits. This paves the way for improved overall health and a stronger sense of food security.
Start today by swapping out one processed meal for a homemade one!
Improving Overall Health and Well-being
Incorporating whole foods into your diet can greatly enhance your health. These foods deliver essential nutrients and lower the risk of chronic diseases.
This approach encourages eating a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, and lean proteins. These options are rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
The fiber in whole foods boosts digestion and helps maintain a healthy weight. This significantly lowers the risk of obesity.
Research shows that such a diet reduces the risk of chronic diseases like diabetes and heart disease. It s a proactive choice for securing long-term health benefits.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are processed foods and how do they differ from unprocessed foods?

Processed foods are foods altered from their natural state through methods like canning, freezing, and adding preservatives. They often have added sugars, salts, and unhealthy fats, which can make them less nutritious than unprocessed foods.
How do processed foods impact our health?
Processed foods can negatively affect health due to high levels of sodium, sugar, and unhealthy fats. These factors contribute to health issues like obesity, heart disease, and diabetes.
Can processed foods be part of a healthy diet?
Yes, processed foods can fit into a healthy diet if consumed in moderation. Always read labels and choose options with lower sodium, sugar, and unhealthy fats.
How do processed foods affect weight and weight loss?
Processed foods are often high in calories but low in nutrients. This makes it easy to overeat, leading to weight gain and hindering weight loss efforts.
Are there any benefits to consuming processed foods?
Some processed foods offer convenience and affordability. Fortified cereals and dairy products, for instance, may contain added vitamins and minerals beneficial for those with nutrient deficiencies.
How can I reduce my consumption of processed foods?
To cut down on processed foods, read labels carefully. Cooking at home with whole ingredients is a great way to avoid processed options.
Planning meals and snacks ahead helps avoid relying on processed foods for convenience.